

So if there isn’t one specific structure that is causing your low back pain, why does your MRI show SO MANY things wrong with your back!? Usually the cause is a combination of multiple different factors – mobility of the surrounding joints (hips, thoracic spine), training error, poor mechanics, personal experience/expectations of back pain – just to name a few. I know how frustrating or confusing that might sound to hear and the reason I wrote this article is to help you have a better understanding of your MRI results and what they mean to your treatment plan.Ī high percentage of low back pain is non-specific – meaning healthcare professionals cannot pinpoint one specific structure to the cause of your pain. And the MRI results could lead the person down the road of surgery or injections or painkillers….when those might not even be necessary. Unfortunately, many of these MRIs are completely UNNECESSARY and could potentially do more harm than good when it comes to getting rid of your pain. It is estimated that about 80% of people will experience low back pain at some point in their lives and many of these people will see a physician who will recommend they get an MRI. What should you think of these really big, negative sounding words like degenerative, spondylosis (the fancy term for arthritis in the spine), narrowing, etc? Quickly you became confused, overwhelmed, and/or anxious reading all these “bad” things about your back. So you just had an MRI of your lumbar spine (lower back) and you went to see the doctor for the results or tried to read the MRI results yourself.
#How to read mri images of lumbar spine how to
You can better visualize certain parts of the vertebra and can identify disc herniations that may not be obvious in the sagittal view.What You NEED To Know About How To Interpret Your Back MRI Results The axial view provides a cross sectional view of the spinal canal and the tunnels through which nerve roots exit. It is also helpful for examining the discs for degenerative changes and can be a helpful angle to see disc herniations protruding into the spinal canal. It allows you to evaluate the curvature of the spine as well as determine if there are any fractures or compression of the vertebral bodies. The sagittal view of the spine is useful for looking at the spinal column in totality. The top down view of the body is known as the “axial” view, and a right-to-left view is known as the “sagittal” view. In addition to different sequences, there are various views of the body depending on the direction of the slices.

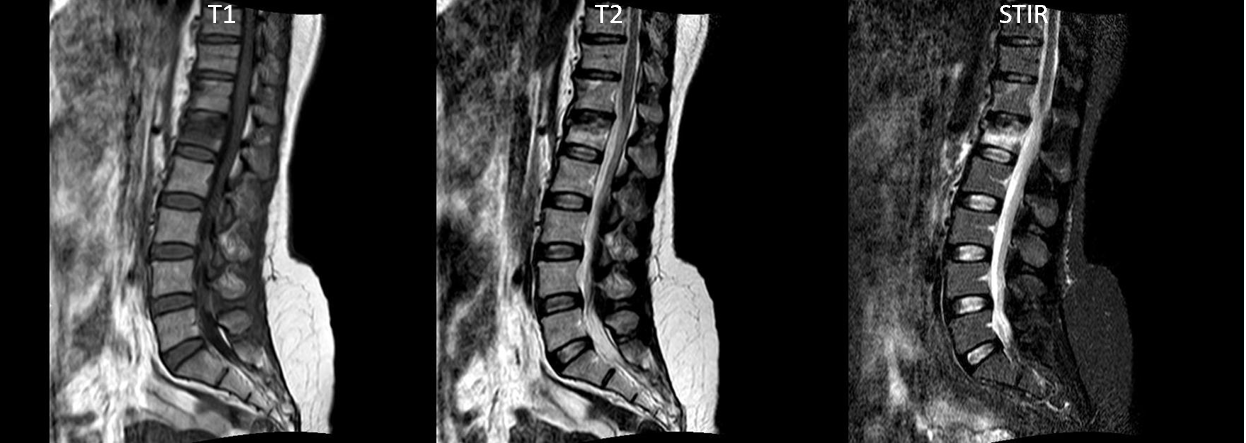
Fatty tissues show up brighter in T1 whereas fatty and water-based tissues show up brighter on T2. Two of the most common sequences are T1-weighted and T2-weighted. A sequence is a particular setting of the MRI which produces variance in the contrast for different tissues. You’ll notice that there are various sets of images with different contrast between tissues (sequences) and look at the body from different angles (views).
#How to read mri images of lumbar spine series
As a result, they typically contain esoteric medical terminology that’s unfamiliar to the average person.ĭo you have a spine MRI report that you are trying to understand? Try our translation service for only $19.Īn MRI image series is made up of various cross sectional “slices” or “cuts” that expose the anatomy various ways. Even these reports can be difficult to understand as they are typically written for other physicians and not usually intended to be read by patients directly. MRI is one of the more complicated imaging modalities to interpret, which is why a report is generally provided by a radiologist, who has undergone many years of medical and specialty training.

If you have undergone an MRI, understanding the results can be challenging. This is why MRI is often considered the “gold standard” in diagnosing problems with the spine. Since protons are abundant in fat and water, MRI does a great job of visualizing tendons, ligaments, nerves, and intervertebral discs. The machine excites protons in the tissues of the body, and sensors measure their energy. MRI, which stands for magnetic resonance imaging, uses a magnetic field and radio waves to create images of the body. MRI does a better job of analyzing the soft tissues, but can be difficult to obtain given long wait times and high cost. For example, xrays, which are accessible and relatively inexpensive, do a good job detecting bone abnormalities but are inadequate to diagnose soft tissue problems. Each imaging technology has its own set of strengths and weaknesses. Different imaging modalities, such as x-ray, CT, and MRI, are used to diagnose different medical conditions.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
